Dental fillings are a common solution for restoring decayed teeth, yet their longevity varies based on several factors. Different materials, such as ceramic, gold, amalgam, and composite, each offer distinct durability. While some fillings last over two decades, others may need replacement in just a few years. Oral hygiene, dietary habits, and regular dental visits greatly influence how long fillings remain effective. Understanding these elements is essential for maintaining ideal dental health.
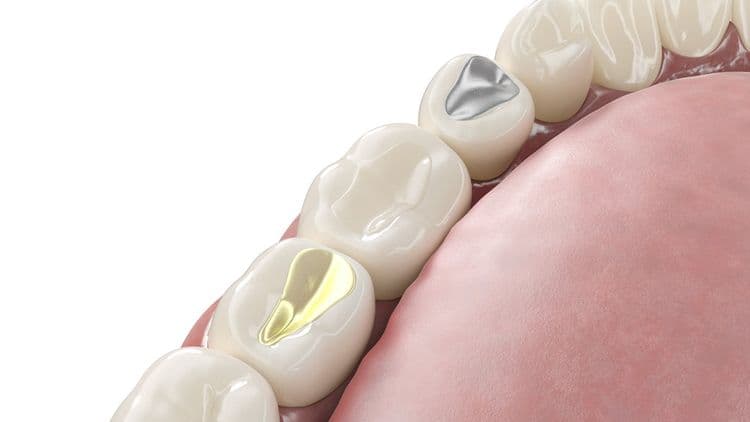
Types of Filling Materials
In the domain of dental restorations, understanding the types of filling materials is essential for determining their longevity and suitability for different clinical scenarios. Ceramic fillings, known for their aesthetic appeal, mimic natural tooth color and are highly resistant to wear. These fillings are ideal for patients seeking durable and visually appealing restorations, particularly in visible areas of the mouth. On the other hand, glass ionomer fillings release fluoride ions, providing an added benefit of caries prevention. They adhere well to tooth structures but are less resistant to wear compared to ceramics, making them suitable for non-load-bearing areas. Clinicians must evaluate patient-specific factors and clinical requirements when selecting between ceramic and glass ionomer fillings to optimize dental restoration outcomes.
Factors Affecting Filling Durability
The longevity of dental fillings is greatly influenced by the type of material used, with amalgam and composite resins offering varying degrees of durability. Evidence suggests that ideal oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing and flossing, play an essential role in maintaining the integrity of fillings by minimizing plaque accumulation. Additionally, variations in bite pressure can lead to stress fractures or displacement, affecting the lifespan of the restoration and necessitating a patient-specific approach to dental care.
Material Type Impact
Although often overlooked, the type of material used for dental fillings greatly impacts their longevity and effectiveness. Filling types such as amalgam, composite resin, gold, and ceramic each possess distinct material properties that influence durability. Amalgam, known for its robustness, can last up to 15 years due to its strong metallic composition. Composite resins offer aesthetic advantages, blending with natural tooth color, but typically endure 5 to 7 years owing to their susceptibility to wear. Gold, while expensive, provides exceptional longevity, often exceeding 20 years, attributed to its corrosion resistance. Ceramic fillings, prized for their natural appearance and strength, generally last 10 to 15 years. These material properties are pivotal in determining the ideal choice for long-lasting dental restorations.
Oral Hygiene Practices
Proper oral hygiene practices are vital in extending the lifespan of dental fillings. Adopting effective flossing techniques can markedly reduce plaque accumulation at the margins of fillings, minimizing the risk of secondary caries. Evidence suggests that daily flossing is essential in maintaining periodontal health and preventing interdental decay, which could compromise filling integrity. Similarly, brushing frequency plays a key role. It is recommended to brush teeth at least twice daily with fluoride toothpaste to effectively remove plaque and prevent demineralization. Failure to adhere to this routine can lead to plaque biofilm formation, increasing the likelihood of restoration failure. A patient-focused approach emphasizes the importance of personalized oral care routines, as individual risk factors may necessitate tailored strategies to guarantee ideal filling longevity.
Bite Pressure Variations
How considerably does bite pressure influence the durability of dental fillings? Evidence suggests that improper bite alignment can greatly affect filling longevity. When bite forces are unevenly distributed, certain areas of a filling may experience increased pressure sensitivity, leading to accelerated wear or fractures. Patients with malocclusion or bruxism exert excessive bite pressure, placing fillings under undue stress. This pressure can cause micro-leakages at the filling margins, thereby compromising the integrity of the restoration. Dental practitioners emphasize the importance of evaluating and correcting bite alignment during filling placement. Regular dental check-ups are essential to monitor pressure distribution and guarantee peak filling performance. Consequently, understanding and managing bite pressure are integral to enhancing the durability of dental fillings, ultimately securing prolonged oral health.
Average Lifespan of Different Fillings
The lifespan of dental fillings varies considerably depending on the material used, with amalgam fillings typically lasting 10 to 15 years due to their robust metal composition. Composite fillings, while offering superior aesthetic appeal, generally have a shorter durability of about 5 to 7 years. These estimates can guide patients in making informed decisions about their dental treatment options, balancing longevity with cosmetic preferences.
Amalgam Fillings Duration
Amalgam fillings, often composed of a mixture of metals including silver, tin, and mercury, generally have a lifespan ranging from 10 to 15 years. This longevity is attributed to the amalgam benefits such as its durability and resistance to wear, making it a preferred choice for molar restorations where chewing forces are significant. However, amalgam drawbacks exist, including potential aesthetic concerns due to their metallic appearance and the release of trace mercury levels, which some studies have scrutinized for patient safety. Clinicians emphasize regular dental assessments to monitor these restorations, addressing wear, marginal integrity, and secondary caries. Evidence suggests that maintaining oral hygiene and attending periodic dental check-ups can maximize the functional lifespan of amalgam restorations in patients.
Composite Fillings Longevity
When considering the longevity of composite fillings, one must recognize their average lifespan typically ranges from 5 to 7 years, although advancements in dental materials and techniques have extended this duration in some cases. Composite advantages include their aesthetic appeal, as they can be closely matched to the natural color of teeth, which is particularly beneficial for visible areas. They also require less tooth preparation, preserving more of the natural tooth structure. However, composite disadvantages involve their susceptibility to wear and staining over time, as well as their tendency to shrink slightly during the curing process, potentially leading to gaps. Clinical decision-making should weigh these factors alongside patient-specific considerations, ensuring an ideal balance between functional longevity and visual outcomes.
Signs Your Filling Needs Replacement
How can one determine if a dental filling is due for replacement? Awareness of specific replacement symptoms is vital. Filling wear is a primary indicator, characterized by the breakdown of material integrity. This degradation may manifest as noticeable cracks, chips, or even dislodgement of the filling. Patients may also experience increased sensitivity to temperature or pressure, suggesting compromised sealing and the possible infiltration of bacteria. Discoloration around the filling margins can indicate leakage. Pain or discomfort when biting down is another symptom that necessitates attention, as it may point to structural failure. Regular dental check-ups are essential for early detection of these signs. Dentists employ diagnostic tools, such as X-rays, to ascertain the condition of fillings, ensuring timely intervention and ideal oral health maintenance.
The Role of Oral Hygiene in Filling Longevity
Proper oral hygiene plays an essential role in the longevity of dental fillings, as it helps maintain the integrity of both the filling material and the surrounding tooth structure. Evidence suggests that consistent oral care, including effective brushing frequency and flossing techniques, is vital in preventing recurrent caries and periodontal disease. Brushing at least twice daily with fluoride toothpaste minimizes plaque accumulation, thereby reducing acid exposure to the filling margins. Concurrently, employing correct flossing techniques removes interdental plaque, important for protecting the proximal surfaces around fillings. Neglecting these practices can lead to secondary caries, jeopardizing the filling’s lifespan. Dental professionals recommend regular dental check-ups to assess the condition of fillings, ensuring early intervention if deterioration is detected, and reinforcing oral hygiene education.

Impact of Diet on Fillings
Although often overlooked, dietary habits greatly influence the longevity of dental fillings. Evidence indicates that high sugar intake can expedite the deterioration of restorative materials. When carbohydrates are consumed, oral bacteria metabolize them into acids, which can undermine the structural integrity of fillings. This acidogenic challenge is exacerbated by frequent snacking on sugary foods, leading to recurrent exposure and increased risk of secondary caries. Furthermore, acidic beverages such as sodas can erode both tooth enamel and filling margins, compromising their lifespan. Conversely, a diet rich in fiber and low in fermentable carbohydrates is associated with reduced cariogenic potential. Patients are advised to moderate sugar intake and choose nutrient-dense foods, thereby enhancing the durability and effectiveness of dental restorations.
How Regular Dental Checkups Help
Regular dental checkups play a pivotal role in extending the lifespan of dental fillings. Through preventive care, a dentist can identify early signs of wear or decay around fillings. This proactive approach allows for timely interventions, ensuring ideal dental maintenance and minimizing the likelihood of filling failure. During checkups, professionals assess the integrity of existing fillings using advanced diagnostic tools, which can detect micro-leakages or fractures not visible to the naked eye. Evidence supports that regular examinations reduce the incidence of secondary caries, a leading cause of filling replacement. By emphasizing a patient-focused strategy, dental practitioners can provide guidance on oral hygiene practices tailored to individual needs. Consequently, patients benefit from prolonged filling efficacy, maintaining oral health and functionality.
Cost Considerations for Filling Replacement
Understanding the financial implications of filling replacement is important for informed decision-making regarding dental care. Filling costs are influenced by various factors including the type of material used, the complexity of the procedure, and geographical location. Common materials such as amalgam, composite resin, and gold vary in price, with composite resins often being more expensive due to aesthetic advantages. Replacement expenses can increase if additional dental work is required, such as the removal of decay or tooth restructuring. Insurance coverage can mitigate some costs, but out-of-pocket expenses remain a consideration for many patients. Evidence suggests that preventive care and regular dental check-ups can extend the lifespan of fillings, thereby delaying the need for costly replacements and minimizing overall dental expenditure.
Tips for Extending the Life of Your Fillings
Maintaining the longevity of dental fillings requires adherence to specific oral hygiene practices and lifestyle modifications. Effective filling maintenance tips include brushing with fluoride toothpaste at least twice daily and flossing to remove interproximal plaque, reducing the risk of secondary caries. Regular dental care practices, such as biannual professional cleanings and evaluations, enable early detection of potential issues, such as marginal leakage or excessive wear. Patients should minimize consumption of cariogenic foods and acidic beverages, which can compromise the structural integrity of fillings. Avoiding parafunctional habits, like bruxism, further extends filling lifespan. Evidence suggests that employing these strategies not only preserves the functionality of the fillings but also contributes to overall oral health, ultimately reducing the need for premature restorative interventions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Fillings Cause Allergic Reactions?
Filling materials can occasionally trigger allergic reactions in patients, presenting allergic symptoms such as itching, redness, or swelling. Evidence suggests these reactions are rare. Patients should consult dental professionals to identify safe materials based on individual sensitivities.
Are There Fillings That Release Fluoride?
Certain dental fillings, such as glass ionomer and resin-modified glass ionomer, are designed to release fluoride. This fluoride release can enhance dental health by strengthening enamel and reducing the risk of further decay in patients.
How Do Fillings Affect Tooth Sensitivity?
Tooth sensitivity causes can be influenced by filling materials impact. Materials like composite resin or amalgam can alter thermal conductivity, potentially increasing sensitivity. Patient-focused care involves selecting appropriate materials and techniques to minimize discomfort and enhance oral health.
Can Fillings Change the Color of My Tooth?
Fillings can cause tooth discoloration depending on the filling materials used. Amalgam fillings may lead to a grayish tint, while composite resins are designed to match tooth color, minimizing noticeable changes and maintaining aesthetic appearance.
Are There Eco-Friendly Filling Options Available?
Eco-friendly filling options are increasingly available, utilizing biodegradable materials that align with sustainable dentistry practices. These materials minimize environmental impact while maintaining efficacy and safety, providing patients with alternatives that support both oral health and ecological responsibility.