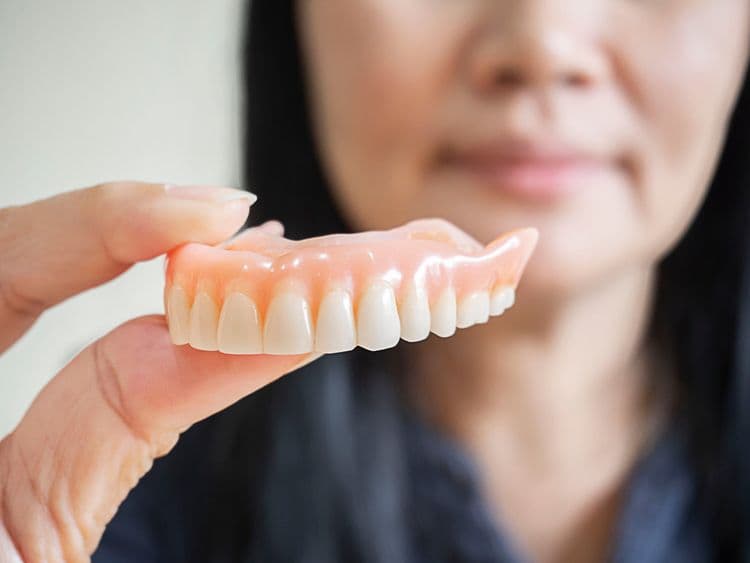
Dentures, composed of materials like acrylic resin and porcelain, can exhibit fluorescence under ultraviolet (UV) or blacklight exposure. This phenomenon arises from specific additives or the inherent properties of these materials, leading to the emission of visible light. Understanding this interaction between blacklight and denture materials not only provides insight into dental appliance aesthetics but also raises questions regarding the practical applications of this fluorescence in oral health monitoring and dental forensics.
Understanding Ultraviolet Light and Fluorescence
Ultraviolet (UV) light, a form of electromagnetic radiation, is characterized by wavelengths shorter than visible light but longer than X-rays, typically ranging from 10 to 400 nanometers. Ultraviolet radiation is integral in eliciting fluorescence effects, wherein certain materials absorb UV light and subsequently emit it as visible light. This phenomenon is essential in various diagnostic and analytical applications, including the evaluation of dental materials. Dentures, composed of polymers and other constituents, may exhibit fluorescence under UV exposure due to specific additives or inherent material properties. The fluorescence effects are contingent on the photophysical interactions within the molecular structure of the denture materials. Understanding these interactions aids in discerning the visual characteristics of dentures under UV illumination, vital for aesthetic dental assessments.
The Composition of Dentures
Dentures are typically fabricated from acrylic resin, porcelain, or a combination of both materials due to their durability and aesthetic properties. The color properties of these materials are designed to mimic natural dental tissues, though they may exhibit varying degrees of fluorescence under ultraviolet light. Manufacturing processes involve meticulous layering and curing techniques to achieve a structurally sound and cosmetically appealing dental prosthesis.
Materials Used in Dentures
Modern denture fabrication relies on a carefully selected composition of materials designed to mimic the natural appearance and functionality of human teeth. Acrylic resin is primarily utilized due to its favorable biocompatibility, ease of manipulation, and cost-effectiveness. This polymer provides the base structure of dentures, offering durable and adaptable support. In contrast, porcelain teeth are often employed for their superior aesthetic qualities, including translucency and hardness that closely resemble natural enamel. These ceramic components are favored for their wear resistance, allowing for prolonged use without significant degradation. The combination of acrylic resin and porcelain teeth results in prosthetics that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing, providing patients with reliable dental restoration solutions that align with contemporary standards of oral health care.
Color Properties of Dentures
In considering the materials used in denture fabrication, attention must also be given to the color properties that these materials exhibit. Denture bases and teeth are primarily composed of acrylic resins and composites, which greatly influence color perception. The optical properties of these materials determine how light reflection occurs, impacting the apparent shade and translucency. Effective replication of natural dentition requires meticulous attention to these factors to guarantee a realistic appearance under various lighting conditions. Denture materials are engineered to mimic the complex interplay of light absorption and scattering found in natural teeth. Variations in hue, chroma, and value are calibrated to achieve esthetic outcomes that meet patient expectations, emphasizing the clinical importance of understanding color properties in prosthodontic applications.
Denture Manufacturing Processes
Crafting dentures involves a series of precise manufacturing processes that hinge upon the careful selection and manipulation of materials. The initial phase begins with denture design, which requires thorough oral assessments to achieve optimal function and aesthetics. Materials such as polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) are mainly employed due to their biocompatibility and strength. The process advances to custom fittings, necessitating detailed impressions of the patient’s oral cavity to guarantee accurate adaptation and comfort. These impressions are used to create molds, which are further refined to enhance the denture’s stability and retention. Adjustments are meticulously executed to accommodate unique anatomical variations, resulting in prosthetics that integrate seamlessly with the oral environment. This evidence-based approach guarantees the production of durable and functional dental appliances.
Materials Used in Denture Fabrication
While advancements in dental technology have evolved considerably, the materials used in denture fabrication remain grounded in their fundamental properties and functionality. Acrylic resins dominate as the primary denture materials due to their biocompatibility, ease of manipulation, and aesthetic qualities. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is frequently employed in denture bases, providing strength and resilience. In addition, porcelain and composite resins are utilized for denture teeth, known for their wear resistance and lifelike appearance. Evidence-based studies highlight the durability and minimal adverse reactions associated with these materials. Rigorous standards guide the selection of materials during denture fabrication, ensuring ideal patient outcomes. Consequently, these materials facilitate the creation of prosthetics that meet clinical performance requirements and patient satisfaction criteria, adhering to stringent dental industry standards.
How Blacklight Interacts With Denture Materials
The interaction between blacklight and denture materials is an intriguing area of study, particularly due to the unique properties of the substances used in their fabrication. Denture visibility under blacklight is influenced by the fluorescence effects of materials like acrylic resins and porcelain. These materials contain compounds that can emit visible light when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. This phenomenon is critical for understanding how dentures appear under specific lighting conditions, such as in dental practice or forensic settings. Fluorescence effects can vary considerably depending on the chemical composition and manufacturing processes of the denture materials. By analyzing these interactions, dental professionals can better predict and control the aesthetic outcomes of dentures, ensuring they meet both functional and cosmetic standards in diverse environments.
The Science Behind Fluorescent Dentures
Understanding the science behind fluorescent dentures involves exploring the principles of photoluminescence and the chemical properties of the materials used in denture fabrication. Photoluminescence refers to a material’s ability to absorb light and re-emit it as visible light, contributing to its fluorescent properties. Specifically, the incorporation of fluorescent dyes or pigments in dental resins enhances the denture aesthetics by mimicking natural tooth fluorescence. When exposed to a blacklight, these materials can exhibit a noticeable glow. This phenomenon is attributed to the structured arrangement of phosphorescent compounds, such as europium-doped strontium aluminate. Rigorous testing and selection of these materials guarantee that dentures not only achieve aesthetic appeal but also maintain functional integrity without compromising oral health. This approach exemplifies the integration of material science in prosthodontics.
Historical Perspectives on Denture Materials
The evolution of denture materials reflects significant advancements in dental prosthetics, shifting from rudimentary components such as ivory and animal bones to the use of vulcanite rubber in the 19th century. Early dentures, often crafted from suboptimal materials, were gradually replaced by acrylic resins and porcelain in the 20th century, enhancing both functionality and aesthetics. Modern innovations have introduced high-performance polymers and biocompatible metals, optimizing durability and mimicking natural dentition under various lighting conditions, including blacklight.
Evolution of Denture Materials
Over the centuries, denture materials have undergone significant transformations, reflecting advances in technology and material science. In the context of denture history, initial materials such as ivory and bone have been supplanted by more sophisticated alternatives. The advent of vulcanite in the mid-19th century marked a pivotal shift, offering increased durability and malleability. Further material advancements emerged with the introduction of acrylic resins in the 20th century, providing superior esthetics, biocompatibility, and ease of fabrication. The integration of ceramic and composite materials has enhanced the structural integrity and appearance, addressing both functional and aesthetic needs. Modern innovations in polymers and computer-aided design have continued to refine prosthodontic outcomes, ensuring that contemporary dentures meet rigorous clinical standards and patient expectations.
Early Denture Components
In examining early denture components, the progression from rudimentary materials to sophisticated options becomes evident. Initially, early materials included natural substances such as bone, ivory, and even human teeth, reflecting historical techniques that prioritized availability over functionality. These materials, often sourced from animals or cadavers, were susceptible to wear, discoloration, and limited integration with oral tissues. Historical techniques involved manual carving and fitting, which lacked precision and often resulted in discomfort or instability. The introduction of vulcanite in the mid-19th century marked a pivotal technological advancement, as this rubber-based material offered improved adaptability and durability. Despite its advantages, vulcanite still presented challenges, such as color mismatches and potential allergenic responses. These early explorations laid the foundation for subsequent innovations in denture fabrication.
Modern Denture Innovations
As advancements in dental materials and technology have progressed, modern denture innovations have seen significant shifts from historical practices, underscoring the importance of biocompatibility and aesthetic integration. Contemporary dentures prioritize denture aesthetics through the use of advanced polymers and ceramics, which closely mimic natural tooth appearance and function. These materials not only enhance the visual appeal but also improve the durability and comfort of prosthetics. Innovative designs incorporate digital imaging and 3D printing technology, allowing for precise customization tailored to individual anatomical structures. This customization guarantees ideal fit and function, reducing common issues such as slippage or discomfort. In addition, the integration of antimicrobial properties within materials aims to enhance oral hygiene, providing a thorough approach to modern denture solutions.

Implications for Denture Wearers
Significantly, the fluorescence of dentures under blacklight holds substantial implications for denture wearers, particularly in social and medical contexts. From a denture hygiene perspective, the visibility of biofilm or plaque accumulation under blacklight can serve as an indicator of oral hygiene effectiveness. This can guide both wearers and dental professionals in improving cleaning protocols. Additionally, in social settings, the unexpected luminescence of dentures might influence social perceptions, potentially causing self-consciousness or embarrassment among wearers if not anticipated. The contrast between natural teeth and dentures under blacklight could lead to increased awareness and motivation for regular dental check-ups. Furthermore, understanding this phenomenon can enhance communication between patients and dental practitioners, optimizing both aesthetic and hygienic outcomes for denture wearers.
The Role of Blacklight in Dental Forensics
The luminescence of dentures under blacklight extends beyond hygiene and social contexts, finding a significant application in the field of dental forensics. Blacklight applications in forensic dentistry facilitate the identification of human remains when traditional methods are inconclusive. Dentures, often composed of polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), exhibit fluorescence under ultraviolet light, providing essential data points for forensic odontologists. Such luminescent properties enable the differentiation of dental prosthetics from bone or other biological tissues in complex scenarios, aiding in victim identification. Additionally, blacklight serves to reveal restorative dental work that may not be visible to the naked eye. These applications underscore the importance of integrating blacklight technology into forensic protocols, enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of forensic investigations.
Exploring Other Everyday Items That Glow
What other everyday items exhibit luminescent properties under blacklight? Certain items reveal unexpected fluorescence due to their chemical composition. Glowing plants, for instance, utilize chlorophyll, which emits a red fluorescence when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. This phenomenon is attributable to the excitation of chlorophyll molecules, a process extensively studied in botanical sciences. Similarly, fluorescent minerals such as fluorite and calcite exhibit luminescence due to the presence of specific impurities or activators like manganese or europium. These minerals are frequently analyzed in geology to understand the mineralogical composition and environmental conditions of formation. These items’ fluorescence is leveraged in various scientific disciplines for qualitative analysis, demonstrating the practical applications of blacklight beyond mere curiosity or decorative use.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Blacklight Exposure Damage Dentures?
Blacklight exposure typically poses no risk to denture materials. Evidence-based studies indicate that common denture materials, such as acrylic resins, are chemically stable and unaffected by blacklight effects, ensuring structural integrity remains uncompromised under such lighting conditions.
Are There Health Risks Associated With Glowing Dentures?
Health implications and safety concerns related to glowing dentures under blacklight are minimal. Clinical evaluations indicate no significant adverse effects. However, further research may be necessary to fully understand long-term exposure outcomes on dental materials and oral tissues.
How Can I Test if My Dentures Glow at Home?
To determine luminescence, individuals can employ DIY testing using home methods. Obtain a UV blacklight, darken the room, and observe dentures under the light. Luminescence indicates fluorescence, a phenomenon associated with certain materials in denture composition.
Do All Types of Dentures Glow Under Blacklight?
The luminescence of dentures under blacklight varies based on the types of materials used. Acrylic resin, porcelain, or composite materials may exhibit differing fluorescence. Proper denture maintenance can affect their optical properties, potentially altering their response to blacklight.
Can Glowing Dentures Help Detect Dental Issues?
Glow detection in dental health primarily aids in identifying restorative material integrity, not direct dental issues. Fluorescence under blacklight can reveal discrepancies in dentures, potentially indicating wear or the need for professional evaluation and adjustment.