The decision between composite bonding and veneers involves evaluating various factors such as procedure details, costs, durability, and effects on natural teeth. Composite bonding offers a cost-effective, immediate solution for minor dental imperfections, while veneers provide a more durable and aesthetically pleasing outcome for extensive issues. Understanding the nuances of each option, including longevity and impact on dental structure, is essential for individuals seeking the best enhancement for their smile.
Understanding Composite Bonding
Composite bonding is a dental procedure that involves the application of a tooth-colored resin material to the surface of teeth to improve aesthetics or repair damage. This method utilizes composite materials, which are a blend of plastic and fine glass particles, chosen for their durability and resemblance to natural tooth enamel. The application techniques involve meticulous preparation of the tooth surface, which may include etching to enhance adhesion. The resin is then carefully sculpted and hardened using a curing light, ensuring a seamless integration with the existing tooth structure. Evidence-based studies suggest that when executed precisely, composite bonding effectively restores tooth function and appearance, providing a conservative alternative to more invasive procedures while preserving the majority of the original tooth.
Exploring Veneers
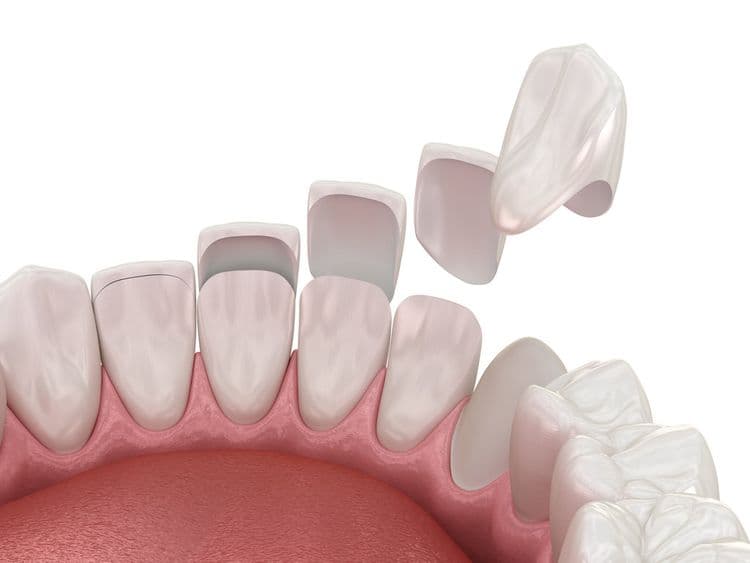
When considering dental aesthetics, veneers offer a transformative option by covering the front surface of teeth with thin shells made from porcelain or composite resin. Veneer types primarily include porcelain veneers and composite veneers, each with distinct characteristics and applications. Porcelain veneers are fabricated from high-quality ceramic materials, offering durability and the ability to mimic the natural translucency of enamel. This veneer material is highly resistant to staining and provides a long-lasting solution for various cosmetic concerns. Composite veneers, conversely, utilize a resin material that is applied directly to the teeth and sculpted to the desired shape. Though less durable than porcelain, composite veneers are more cost-effective and allow for quicker placement. The choice between veneer types depends on individual patient needs and aesthetic goals.
Comparing Procedures
Understanding the procedural differences between composite bonding and veneers is essential in determining the appropriate dental treatment for enhancing aesthetic appearances. Composite bonding involves applying a tooth-colored resin to the tooth’s surface and hardening it with a special light, allowing for immediate results in a single visit. This treatment option is minimally invasive, preserving more of the natural tooth structure. Veneers, conversely, require the removal of a thin layer of enamel before custom-fabricated porcelain shells are affixed to the teeth, typically necessitating multiple appointments.
Patient preferences play a significant role in selecting between these options. Composite bonding may appeal to those seeking quick, reversible solutions, while veneers offer a more durable, stain-resistant alternative, often preferred by patients desiring a longer-lasting cosmetic enhancement.
Cost Considerations
Financial implications are a critical factor when evaluating composite bonding and veneers. Composite bonding is generally more cost-effective, offering a lower upfront expense compared to veneers. This procedure involves applying a resin material directly onto the teeth, which translates to reduced laboratory and material costs. Conversely, veneers, crafted from porcelain or similar materials, necessitate a more intricate fabrication process, greatly increasing the financial outlay. Evidence suggests that veneers can be up to three times more expensive than composite bonding due to these complexities. Budget considerations are paramount, as individuals must weigh immediate financial constraints against potential future expenses associated with maintenance or replacement. Understanding these cost differences aids patients in making informed decisions aligned with their financial capabilities and aesthetic objectives.
Durability and Longevity
Cost considerations often guide the initial choice between composite bonding and veneers; however, the durability and longevity of these dental treatments are equally significant factors in decision-making. Composite bonding, characterized by its application of resin materials, typically presents a lifespan ranging from 5 to 7 years. Durability factors include susceptibility to chipping and discoloration due to material composition. Conversely, veneers, constructed from porcelain, exhibit greater resistance to wear and staining, with longevity expectations extending to 10-15 years. Clinical studies highlight porcelain’s superior hardness and stability, contributing to its extended lifespan. Nevertheless, both treatments require periodic evaluation to address potential issues such as debonding. As a result, understanding the inherent durability factors and longevity expectations is essential for informed dental treatment planning.
Aesthetic Outcomes
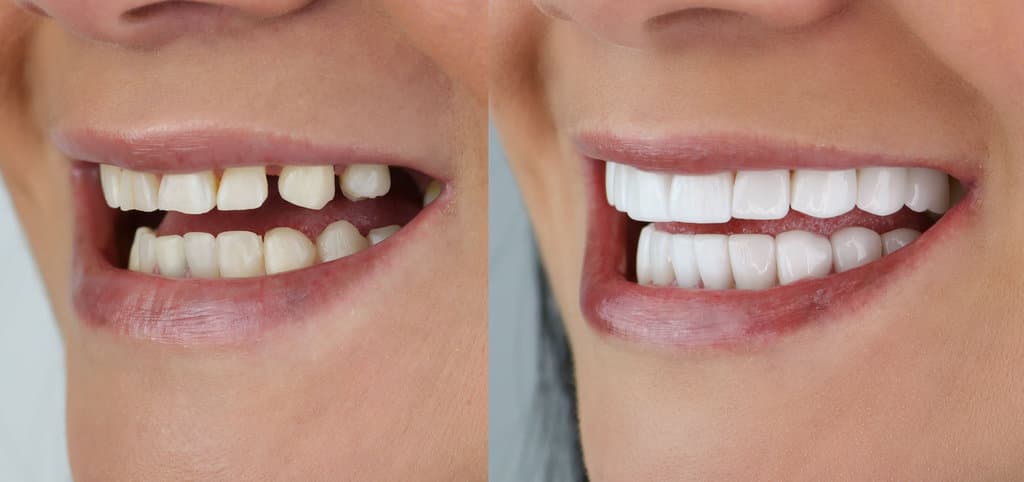
When considering aesthetic outcomes, it is essential to evaluate the visual appeal that composite bonding and veneers can achieve. Composite bonding, crafted from resin, offers a customizable approach that allows for precise color matching to adjacent teeth. However, it may lack the translucency and depth of color that porcelain veneers provide, potentially affecting its aesthetic appeal. Veneers, composed of high-grade porcelain, offer superior visual impact by mimicking the natural enamel’s light-reflective properties. This results in an enhanced, lifelike appearance. Clinical studies suggest veneers offer a more consistent and durable aesthetic outcome over time compared to composite bonding. While both options can greatly improve dental aesthetics, veneers typically provide a more pronounced enhancement regarding overall visual impact and satisfaction.
Impact on Natural Teeth
When evaluating the impact on natural teeth, composite bonding and veneers exhibit distinct differences in tooth structure preservation and enamel removal requirements. Composite bonding typically involves minimal alteration of the natural tooth, preserving most of the original enamel, which is advantageous in maintaining tooth integrity. Conversely, veneers generally necessitate a more invasive preparation process, including significant enamel reduction, to guarantee proper adhesion and aesthetic fit, which can impact the long-term health of the tooth.
Tooth Structure Preservation
Although both composite bonding and veneers are popular cosmetic dental treatments, their impact on the preservation of natural tooth structure varies greatly. Composite bonding is minimally invasive, typically requiring little to no removal of the natural tooth structure, thereby preserving its integrity. This method can lead to minimal tooth sensitivity post-treatment, which is a notable consideration for patient comfort. In contrast, veneers often necessitate a more invasive approach, potentially impacting the underlying tooth structure more profoundly. The longevity of these treatments differs as well; composite bonding may require periodic maintenance due to its susceptibility to staining and wear over time. Conversely, veneers, while more enduring with proper care, may involve greater initial compromise of tooth structure, affecting long-term dental health.
Enamel Removal Requirements
The preservation of tooth structure is closely linked to the extent of enamel removal required by cosmetic dental procedures. Veneers necessitate significant enamel reduction, often involving the removal of 0.5 to 0.7 mm of enamel thickness. This irreversible process can potentially predispose the tooth to heightened enamel sensitivity due to exposure of underlying dentin. In contrast, composite bonding typically demands minimal enamel removal, preserving more of the natural tooth structure. This conservative approach reduces the risk of postoperative enamel sensitivity and maintains functional integrity. Studies have demonstrated that minimal intervention correlates with lower incidences of sensitivity and long-term tooth health. Hence, the choice between veneers and composite bonding should consider the clinical implications of enamel preservation versus removal.
Suitability for Different Dental Issues
The suitability of composite bonding and veneers for various dental issues hinges on the specific condition being addressed. For tooth discoloration, veneers offer a more permanent and stain-resistant solution compared to composite bonding, which may require periodic maintenance. In cases of chipped teeth, both treatments can be effective, but composite bonding is often preferred for minor repairs due to its conservative nature and ease of application.
Addressing Tooth Discoloration
When evaluating the best approach for addressing tooth discoloration, one must consider the underlying cause and severity of the discoloration. For extrinsic stains caused by dietary habits or smoking, tooth whitening procedures can effectively achieve stain removal. These techniques, often using hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, oxidize and lighten surface stains. However, intrinsic discoloration, stemming from factors such as trauma or medication use, may not respond adequately to tooth whitening. In such cases, veneers offer a more thorough solution by covering the tooth surface with a thin, custom-made shell, thereby masking discoloration. Composite bonding serves as another alternative, wherein a resin material is applied and sculpted directly onto the tooth, providing localized stain concealment. Each method’s efficacy depends on the discoloration’s etiology and extent.
Fixing Chipped Teeth
Addressing chipped teeth requires a clinical assessment to determine the most suitable restorative technique, depending on the extent of the damage and the tooth’s functional demands. Composite bonding is often recommended for minor chips due to its conservative nature and ability to closely mimic natural dental aesthetics. This technique involves the application of a tooth-colored resin, which is sculpted and hardened with a curing light to restore the tooth’s original shape and function. Veneers, conversely, may be indicated for larger or more visible chips, especially when enhanced aesthetics are desired. These custom-made porcelain laminates cover the tooth’s front surface, providing improved durability and a seamless appearance. Both methods aim to restore the tooth’s structural integrity and aesthetic appeal efficiently.
Correcting Misaligned Teeth
Correcting misaligned teeth necessitates a thorough assessment of the patient’s occlusion, dental history, and aesthetic goals to determine the most appropriate intervention. Misalignment solutions vary based on the severity and nature of the dental issue. Orthodontic alternatives, including traditional braces and clear aligners, are often considered the first-line treatment for significant misalignments, focusing on long-term functional and aesthetic outcomes. However, for minor misalignments, composite bonding and veneers offer viable options. Composite bonding involves the application of a tooth-colored resin to reshape and align teeth, providing a minimally invasive, cost-effective solution. Veneers, although more invasive, offer enhanced durability and aesthetic improvements. Evidence-based decision-making should guide the choice between these interventions, considering patient-specific needs and the potential for achieving ideal dental harmony.
Making the Right Choice for Your Smile
How does one determine the most suitable option for enhancing their smile: composite bonding or veneers? The decision requires a personalized approach, considering individual aesthetic goals and dental health status. Composite bonding offers a minimally invasive smile transformation, using a tooth-colored resin to repair minor imperfections. It is cost-effective, requires less enamel removal, and is suitable for patients seeking quicker results. Veneers, on the other hand, involve thin porcelain shells adhered to the tooth surface, providing a durable and natural-looking enhancement. They are ideal for patients with significant discoloration or structural issues. Clinical evidence suggests veneers offer superior longevity and aesthetics, but at a higher cost and procedure complexity. A thorough dental evaluation is essential to guide this decision-making process.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Composite Bonding or Veneers Help With Sensitivity Issues?
The current question addresses whether dental procedures can aid in sensitivity relief. Treatment comparison reveals both composite bonding and veneers offer potential benefits. Clinical evidence suggests veneers provide superior coverage, consequently potentially reducing dentin exposure and associated sensitivity more effectively.
How Do Lifestyle Habits Affect the Results of Dental Procedures?
Lifestyle habits critically influence dental procedure outcomes. Poor oral hygiene can lead to plaque accumulation, compromising results. Smoking effects include increased staining and slower healing, reducing the longevity and effectiveness of dental treatments, according to multiple clinical studies.
What Is the Recovery Time After Getting Composite Bonding or Veneers?
Recovery time varies; composite bonding typically requires minimal downtime, while veneers may need a few days. Recovery tips include avoiding hard foods and practicing oral hygiene. The healing process involves tissue adaptation and occlusal stabilization, ensuring procedural success.
Are There Any Dietary Restrictions After the Procedures?
Post-procedure dietary guidelines recommend avoiding hard, sticky, or staining food choices to prevent damage or discoloration. Evidence-based studies suggest that adhering to these guidelines can enhance the longevity and aesthetic outcome of dental treatments.
Can I Switch From Composite Bonding to Veneers Later On?
Switching from composite bonding to veneers is feasible. The bonding comparison reveals that veneers offer greater durability and aesthetic appeal. Veneer advantages include resistance to staining and longevity, making them a preferred choice for long-term dental restoration.