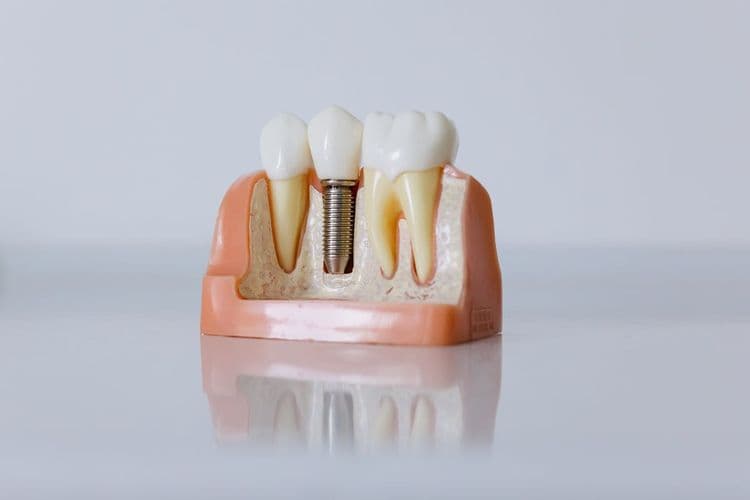
Dental implants are categorized to address diverse clinical scenarios and anatomical considerations. Endosteal implants are embedded within the jawbone for ideal osseointegration. Subperiosteal implants are suitable for patients with limited bone height, resting under the periosteum. Zygomatic implants anchor into the zygomatic bone for severe maxillary bone loss. Mini dental implants offer minimally invasive stabilization. Each type presents unique advantages and indications, prompting further exploration into their specific roles and applications.
Endosteal Implants
Endosteal implants, although widely utilized, serve as the foundational type of dental implant surgically placed into the jawbone. These implants consist primarily of biocompatible materials, such as titanium or titanium alloys, which promote osseointegration—a critical process where the bone fuses with the implant surface. Endosteal implant materials are chosen for their mechanical properties and biological compatibility, ensuring long-term stability and success of the prosthetic restoration. During endosteal implant placement, precision is paramount. The surgical procedure involves meticulous drilling into the jawbone to create a site for the implant fixture, followed by a healing period allowing osseointegration. Subsequent phases include abutment connection and prosthetic crown attachment. This method is favored for its durability and high success rates in dental restoration.
Subperiosteal Implants
Subperiosteal implants, often visualized as metal frameworks, rest on the superior aspect of the jawbone beneath the periosteum. This specific subperiosteal placement is advantageous for patients with insufficient bone height or density unsuitable for endosteal implants. The subperiosteal design circumvents the need for bone grafting, which is a significant subperiosteal advantage, particularly in cases of severe alveolar ridge resorption.
Fabricated from biocompatible materials, these frameworks are custom-fitted to an individual’s jaw contour through precise imaging techniques. The surgical procedure involves creating an incision to expose the jawbone, followed by the accurate positioning of the implant. Once in place, it serves as a stable anchor for dental prostheses. By offering an alternative in complex clinical scenarios, subperiosteal implants enhance the scope of rehabilitative dental solutions.
Zygomatic Implants
In cases where subperiosteal implants may not provide the necessary support due to extreme maxillary bone loss, zygomatic implants offer a viable alternative. These implants are specifically designed for patients exhibiting severe atrophy of the maxillary alveolar bone, where traditional implant placements are unfeasible. Zygomatic implant placement involves anchoring the implant into the zygomatic bone, which provides a robust and stable foundation for prosthetic rehabilitation. This method bypasses the need for bone grafting procedures, thereby expediting the restoration process. Zygomatic bone integration is critical for achieving long-term success, as it guarantees the stability and functionality of the implant. Clinicians must employ precise surgical techniques to optimize osseointegration and mitigate potential complications associated with this advanced implantology procedure.
Single Tooth Implants
Single tooth implants involve a meticulous procedure where a titanium post is surgically inserted into the jawbone, ultimately supporting a custom prosthetic crown. The healing process, known as osseointegration, typically spans several months, ensuring stability and functionality akin to natural dentition. While offering significant advantages such as preservation of adjacent teeth and bone integrity, the cost can vary, and insurance coverage may be limited, necessitating careful financial consideration.
Procedure and Healing Process
Initiating a single tooth implant procedure involves a meticulous sequence of clinical steps designed to guarantee ideal integration and functionality. Initially, the oral surgeon employs advanced surgical techniques to create an osteotomy in the alveolar bone, carefully positioning the titanium implant fixture. Precision in depth and angulation is essential to ensuring osseointegration. Post-operative care demands scrupulous attention, encompassing instructions for managing swelling, discomfort, and potential infection. Patients are advised on maintaining oral hygiene and dietary modifications to facilitate best healing. The initial healing phase, typically spanning 3 to 6 months, allows for bone regeneration and stabilization of the implant. After successful integration, a custom abutment and crown are affixed, restoring the tooth’s structural and aesthetic attributes. The entire process necessitates rigorous adherence to protocol for successful outcomes.
Benefits of Single Implants
Although dental technologies offer various solutions for tooth restoration, single implants present distinct advantages, particularly regarding preserving oral health and providing long-term functionality. Single tooth implants are engineered to seamlessly integrate with the jawbone, effectively maintaining the structural integrity of adjacent teeth. This osseointegration process prevents bone resorption, a common issue with tooth loss, thereby promoting ideal oral health.
Aesthetic enhancement is another significant benefit; single implants mimic natural teeth in both form and color, ensuring an inconspicuous appearance. Additionally, these implants provide improved functionality by restoring full masticatory efficiency, allowing patients to bite and chew without discomfort or compromise. The stability of single implants eliminates the slipping or shifting often associated with alternative prosthetic solutions, ensuring reliable performance over time.
Cost and Insurance Considerations
When considering single tooth implants, how does one navigate the complexities of cost and insurance? Cost factors are multifaceted, including the implant material, surgical procedure, and geographical location. The average expense for a single tooth implant ranges from $3,000 to $4,500. Insurance coverage for dental implants varies markedly, often contingent upon the insurer’s policy and the patient’s specific plan. Dental insurance may partially cover certain procedures, such as crown placement, but often excludes the implant fixture itself. Patients should conduct a thorough review of their insurance plans to understand potential out-of-pocket expenses. Additionally, some practitioners offer financing options to alleviate upfront costs. Understanding these elements is essential for informed financial planning in the acquisition of dental implants.
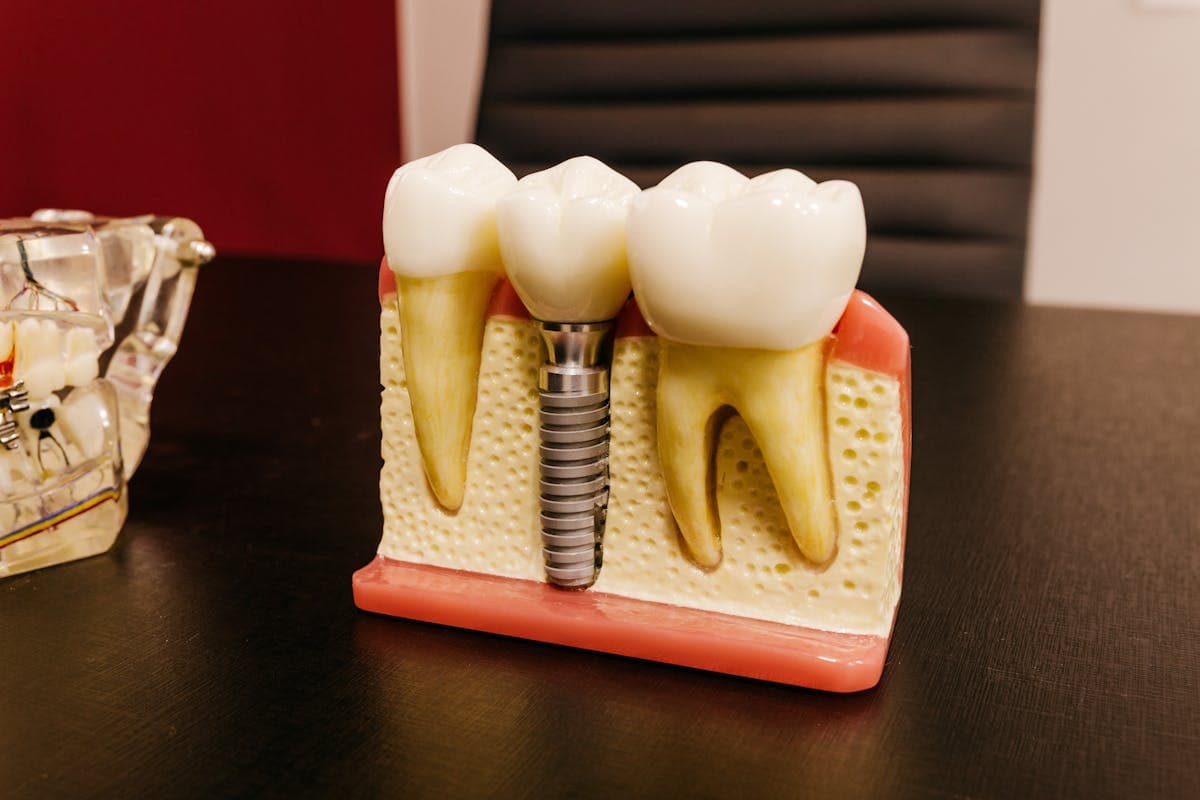
Multiple Tooth Implants
Multiple tooth implants, a vital solution in restorative dentistry, address the replacement of several missing teeth with precision and stability. These implants offer numerous advantages, including improved masticatory function, enhanced esthetics, and preservation of bone structure. By distributing occlusal forces evenly, they mitigate the risk of implant overload, guaranteeing long-term success. However, multiple implants considerations are significant for ideal outcomes. Factors such as bone quality, quantity, and patient-specific anatomical constraints must be thoroughly evaluated through advanced imaging techniques. Additionally, the strategic placement of implants is essential to achieve an ideal prosthetic outcome and esthetic alignment. Moreover, patient compliance with oral hygiene and regular follow-up visits is paramount to minimize peri-implant complications and guarantee the longevity of the implant-supported prostheses.
All-on-4 Implants
The All-on-4 implant technique, a revolutionary approach in oral rehabilitation, provides a full-arch prosthetic solution using only four strategically placed implants. This method optimizes support and stability by angling the posterior implants, which engage denser bone regions. The All-on-4 procedure allows for immediate loading, enabling patients to receive a fixed provisional prosthesis on the same day of surgery.
Among the All on 4 advantages are reduced surgical time, minimal invasiveness, and elimination of bone grafting in most cases. This technique is particularly beneficial for edentulous patients, offering improved masticatory efficiency and aesthetic outcomes. Clinically, the All-on-4 approach enhances patient comfort and satisfaction, while its streamlined treatment protocol reduces overall recovery time, making it a preferred choice in implantology.
Mini Dental Implants
Mini dental implants offer several advantages, including reduced invasiveness and shorter procedure times compared to conventional implants. The implantation process typically involves a minimally invasive technique, resulting in decreased recovery time and less postoperative discomfort. These characteristics make mini implants an attractive option for patients with limited bone density or those seeking expedited dental restoration.
Benefits of Mini Implants
While considering the options for dental restoration, mini implants present numerous advantages that make them a compelling choice for certain patients. Mini implant advantages include their minimally invasive nature, reduced healing time, and suitability for patients with insufficient bone density. Their smaller diameter allows placement in areas where traditional implants might not be feasible without bone grafting. In addition, mini implant durability is commendable, with clinical studies demonstrating comparable longevity to conventional implants when properly maintained. These implants provide a reliable solution for stabilizing dentures or supporting crowns, given their robust structural integrity. Moreover, mini implants often require fewer appointments, thereby reducing patient chair time. Overall, they offer a viable and efficient option for individuals seeking effective dental restoration with enhanced procedural convenience.
Procedure and Recovery Time
Initiating a mini dental implant procedure involves a streamlined and efficient process designed for ideal patient comfort and expedited recovery. The surgical techniques employed are minimally invasive, requiring a small incision in the gingival tissue. This allows for the insertion of the titanium implant without the need for extensive bone modification. The procedure typically necessitates local anesthesia, further enhancing patient comfort. Immediate stability is achieved due to the implant’s design, reducing the need for sutures and promoting rapid osseointegration.
Post operative care is essential for optimal recovery. Patients are advised to adhere to a soft diet and maintain rigorous oral hygiene. Routine follow-ups with dental professionals guarantee the absence of complications, such as infection or implant failure, thereby facilitating a swift return to normal oral function.
Immediate Load Implants
How can dental professionals expedite the restoration process while maintaining ideal outcomes? Immediate Load Implants offer a solution by allowing the placement of a temporary crown shortly after implant insertion. This innovative approach minimizes patient wait time, offering immediate benefits such as enhanced aesthetics and function without compromising implant success. Clinicians must rigorously assess bone quality and the implant’s primary stability to guarantee top results. The technique requires precise surgical and prosthetic protocols to achieve osseointegration and long-term stability. By leveraging advanced materials and technology, dental professionals can provide a streamlined treatment, reducing the overall time frame traditionally associated with implantology. Immediate Load Implants represent a significant advancement in dental restoration, offering patients both efficiency and effectiveness in achieving desired outcomes.
Implant-Supported Dentures
Implant-supported dentures, a sophisticated solution in restorative dentistry, offer enhanced stability and functionality over traditional dentures. These dentures are anchored by dental implants, providing superior implant stability that minimizes movement and enhances oral function. Typically, two to six implants are strategically placed in the jawbone, distributing occlusal forces evenly and reducing pressure on the underlying bone tissue. This distribution aids in preserving bone integrity and maximizing prosthetic performance.
Implant-supported dentures require meticulous denture maintenance to guarantee longevity and top-notch function. Regular professional check-ups are essential for evaluating implant health and prosthetic fit. Patients must adhere to prescribed oral hygiene practices, including thorough cleaning of the denture and surrounding soft tissues, to prevent peri-implant diseases. Consequently, implant-supported dentures represent a durable and effective option for edentulous patients.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Do Dental Implants Typically Last?
Dental implants typically exhibit longevity ranging from 10 to 30 years, contingent on factors such as osseointegration success and adherence to maintenance tips, including diligent oral hygiene, regular dental check-ups, and avoidance of excessive occlusal forces.
What Is the Average Cost of Dental Implants?
The average cost of dental implants varies considerably, often ranging from $3,000 to $5,000 per implant. Dental insurance typically covers limited costs, necessitating patients to explore financing options to manage out-of-pocket expenses effectively.
Are There Any Risks Associated With Dental Implants?
Implant complications related to dental procedures may include infection, nerve damage, or implant failure. Surgical procedures, despite their precision, carry risks such as anesthesia reactions and postoperative discomfort, necessitating thorough patient evaluation and adherence to clinical protocols.
How Do I Care for My Dental Implants?
Proper implant maintenance requires rigorous oral hygiene practices, including brushing twice daily with non-abrasive toothpaste, flossing around the implant, and regular professional cleanings. Guaranteeing ideal peri-implant tissue health minimizes risks of peri-implantitis and guarantees implant longevity.
Can Everyone Get Dental Implants?
Determining implant candidacy requirements involves evaluating bone density, oral health, and age considerations. Not everyone qualifies; individuals must meet specific clinical criteria to guarantee successful osseointegration and long-term implant stability, consequently necessitating professional assessment.