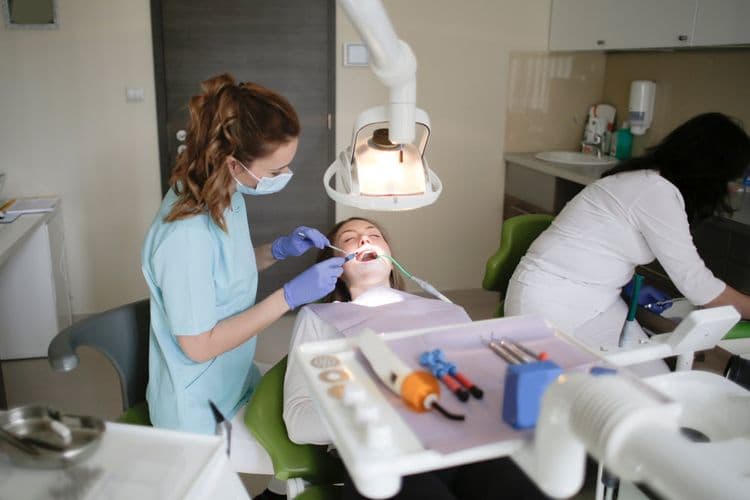
Dental implants, a common solution for tooth replacement, are often perceived as painful. However, clinical evidence suggests otherwise. Anesthesia plays an essential role in minimizing pain during the procedure, making it tolerable for most patients. Post-operative discomfort is typically mild to moderate and comparable to other dental procedures, such as extractions. With effective pain management strategies, patients often find the experience less intimidating than anticipated. What makes this procedure particularly interesting is…
Understanding the Dental Implant Procedure
The dental implant procedure is a multi-step process that, while complex, is well-documented and methodically executed by dental professionals. Initially, the procedure involves the surgical placement of a titanium post into the jawbone, serving as an artificial root. This phase is critical to implant success, relying on the osseointegration process, where the bone fuses with the implant surface, ensuring stability and durability. The healing process can span several months, during which the implant is monitored for proper integration. Clinical studies emphasize the importance of maintaining a sterile environment and precise surgical technique to minimize complications. Successful healing is pivotal, as it directly correlates with the long-term functionality and success of the dental implant, ultimately impacting patient outcomes positively.
The Role of Anesthesia in Minimizing Pain
Anesthesia plays an essential role in mitigating pain during dental implant procedures by utilizing various types such as local, regional, and general anesthesia. The administration techniques are precisely tailored to the patient’s medical history and the complexity of the procedure, ensuring ideal pain control and patient comfort. Evidence-based post-procedure pain management strategies further enhance recovery by alleviating discomfort and promoting healing.
Types of Anesthesia
Various types of anesthesia play a critical role in minimizing pain during dental implant procedures. Local anesthesia is the most commonly employed method, effectively numbing the specific area where the implant will be placed, thereby reducing nociceptive input. This technique allows patients to remain conscious yet free from localized pain sensations during the surgery.
In addition to local anesthesia, sedation options are utilized to enhance patient comfort. Intravenous or oral sedation can be administered to achieve varying levels of consciousness, from minimal sedation to deep sedation, based on patient-specific needs and procedural complexity. Evidence supports the efficacy of these sedation methods in alleviating anxiety and discomfort, facilitating a smoother surgical experience. The selection of anesthesia type is contingent upon clinical assessment and patient preference.
Administering Anesthesia Techniques
Effective management of pain during dental implant procedures relies on the meticulous administration of anesthesia techniques. Clinicians employ a spectrum of sedation options to cater to individual patient needs, guaranteeing ideal comfort and minimizing procedural discomfort. Anesthesia administration involves precise dosing of local anesthetics, such as lidocaine or articaine, to achieve adequate nerve blockade at the surgical site. Advanced sedation options, including nitrous oxide inhalation and intravenous sedation, are utilized to enhance patient relaxation and reduce anxiety. Evidence supports the use of conscious sedation for patients with heightened sensitivity or dental phobia, contributing to improved procedural outcomes. The selection of appropriate anesthesia techniques requires thorough patient assessment, taking into account medical history, procedural complexity, and patient preference to guarantee effective pain management.
Post-Procedure Pain Management
Post-procedure pain management in dental implantology is a critical component of the overall treatment strategy, directly influenced by the anesthesia techniques employed during surgery. Effective anesthesia reduces intraoperative nociceptive input, thereby decreasing postoperative discomfort. Evidence-based pain relief options include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and acetaminophen, which are standard for managing mild to moderate post-surgical pain. Opioids may be considered for severe pain but are less commonly recommended due to potential adverse effects. Adjunctive measures such as cold therapy and elevation may also enhance recovery. Recovery tips emphasize adherence to prescribed analgesic regimens and minimizing physical stress on the surgical site. Clinicians should tailor pain management plans to individual patient needs, optimizing comfort and facilitating rapid recovery.

What to Expect During the Implant Surgery
During dental implant surgery, patients can anticipate a carefully controlled procedure designed to minimize discomfort and guarantee successful integration of the implant. Surgery preparation involves a thorough clinical evaluation, including radiographic imaging to assess bone density and anatomical structures. Patients are informed about procedural steps to align expectations, promoting psychological readiness and compliance.
Local anesthesia is administered to guarantee a pain-free experience, targeting specific oral regions. The clinical team maintains aseptic techniques throughout the surgery to reduce infection risk. Using precision surgical instruments, the clinician creates a pilot hole in the alveolar bone, followed by implant placement with torque measurements to ensure primary stability. Evidence-based protocols guide every aspect, optimizing the osseointegration process and contributing to favorable long-term outcomes.
Immediate Post-Surgery Sensations
Following the completion of dental implant surgery, patients often experience a range of immediate post-surgical sensations that are typical and indicative of the body’s natural response to the procedure. These sensations primarily include localized edema and erythema, which are part of the inflammatory process. Transient post-surgery discomfort is also prevalent, often manifesting as mild to moderate pain localized around the surgical site. This discomfort is typically due to periosteal and soft tissue manipulation during the procedure. In some cases, patients report paresthesia as an immediate sensation, which is usually temporary. Clinically, these responses are considered normal and anticipated within the initial 48 to 72 hours post-operatively. Monitoring these symptoms is crucial to guarantee they resolve without complications, indicating successful initial healing.
Pain Management Techniques for Recovery
How can patients effectively manage pain during the recovery phase of dental implant surgery? Effective pain relief post-surgery involves a combination of pharmacological and non-pharmacological strategies. Clinicians typically recommend nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or acetaminophen as first-line pharmacological agents due to their efficacy in alleviating mild to moderate pain. In some cases, short-term prescription opioids may be prescribed for severe discomfort. Additionally, recovery tips emphasize cold compresses applied intermittently during the first 48 hours to reduce swelling and inflammation. Patients are advised to maintain oral hygiene with gentle rinsing, avoiding vigorous spitting or brushing near the implant site. Stress reduction practices such as deep-breathing techniques may also contribute to effective pain management, enhancing overall recovery outcomes. Clinical evidence supports these strategies for optimizing patient comfort.
How Long Does Discomfort Last?
The duration of discomfort following dental implant surgery typically spans several days to a few weeks. Initial postoperative discomfort is often most intense within the first 48 to 72 hours, aligning with the acute inflammatory phase of wound healing. As the recovery timeline progresses, patients generally experience a gradual reduction in symptoms. Evidence indicates that by the end of the first week, discomfort duration considerably diminishes. However, minor tenderness and swelling may persist for up to four weeks, influenced by individual healing responses and procedural complexity. Clinicians emphasize the importance of adhering to postoperative care instructions to optimize the recovery timeline. Consistent follow-up appointments guarantee effective monitoring, allowing for adjustments to management plans if the discomfort duration exceeds expected parameters.
Comparing Dental Implants to Other Dental Procedures
When evaluating the relative discomfort associated with dental implants compared to other dental procedures, it is essential to take into account the invasiveness of the surgery and the body’s response to it. Dental implants involve osseointegration, a process where the titanium post integrates with the jawbone, potentially leading to postoperative discomfort. Procedure comparisons indicate that root canals and extractions generally result in acute pain due to nerve involvement, whereas implant advantages include a more stable long-term outcome with reduced chronic discomfort once healing concludes. Evidence suggests that while initial post-surgical discomfort from implants can be significant, it is comparable to or less than that experienced with other dental interventions. Healing trajectories emphasize implant advantages regarding durability and functional restoration.
Advice From Dental Professionals on Pain
Why do patients often express concerns about pain associated with dental implants? This apprehension primarily stems from the invasive nature of the procedure, which involves osseointegration, a process where the implant fuses with the jawbone. Dental professionals acknowledge these patient concerns and emphasize that pain perception varies individually. Clinically, pain management is addressed through local anesthesia during surgery and postoperative analgesics. Evidence-based professional recommendations include thorough preoperative assessments, which help in tailoring pain management strategies to individual needs. Additionally, dental practitioners advise maintaining effective communication with patients to alleviate anxiety and guarantee informed consent. Research indicates that adherence to these professional recommendations considerably mitigates discomfort, leading to a more favorable perception of the dental implant procedure among patients.
Patient Experiences With Dental Implants
How do patients perceive their experiences with dental implants? Patient testimonials and personal stories provide valuable qualitative data regarding the subjective experience of dental implant procedures. Evidence suggests that while initial postoperative discomfort is common, the majority of patients report satisfaction with pain management and functional outcomes. Clinical evaluations highlight that individual pain perception varies, influenced by factors such as pain threshold and psychological disposition. Personal stories reveal that effective communication and thorough preoperative education can mitigate anxiety and enhance patient cooperation. Many patients describe the procedure as less painful than anticipated, attributing positive outcomes to the expertise of dental professionals. Overall, patient experiences underscore the importance of tailored care and extensive support throughout the dental implant process.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are There Any Dietary Restrictions Following Dental Implant Surgery?
Following dental implant surgery, patients are advised to consume soft foods to facilitate the healing process. This dietary restriction minimizes pressure on the surgical site, reducing complications and promoting ideal osseointegration, as supported by clinical guidelines and evidence-based practices.
Can Dental Implants Cause Long-Term Nerve Damage?
Long-term nerve damage from dental implants is rare but possible. Nerve sensitivity may occur, particularly if implant placement affects surrounding nerves. Clinical studies indicate precision in placement considerably reduces risks, underscoring the importance of experienced practitioners in mitigating complications.
What Are the Signs of a Dental Implant Infection?
Infection symptoms post-dental implant may include persistent pain, swelling, redness, or pus discharge. These signs can disrupt the healing process, potentially leading to implant failure. Clinical evaluation and timely intervention are essential for best outcomes.
How Should I Clean My Dental Implants Post-Surgery?
Post-surgery implant care involves evidence-based cleaning techniques, including gentle brushing with a soft-bristled toothbrush, using antimicrobial mouthwash, and employing interdental brushes or floss for thorough plaque removal, ensuring ideal healing and long-term implant success.
Are There Any Non-Surgical Alternatives to Dental Implants?
Non-surgical alternatives to dental implants include dental bridges and removable dentures. Dental bridges involve anchoring artificial teeth to adjacent teeth, while removable dentures are prosthetic devices replacing multiple missing teeth, offering less invasive solutions compared to surgical implants.