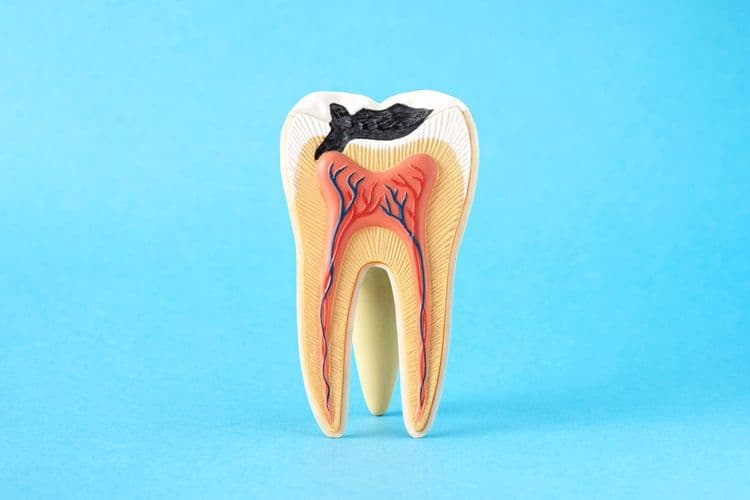
Tooth decay is a prevalent condition caused by bacterial activity on the tooth surface, leading to the demineralization of enamel. Effective management requires a structured oral care routine. Regular use of fluoride toothpaste and flossing disrupts plaque accumulation. Incorporating mouthwash with antibacterial properties enhances this regimen. Adopting a balanced diet low in sugars further minimizes decay risk. Understanding these components is essential to halting decay progression and maintaining dental health.
Understanding the Causes of Tooth Decay
Tooth decay, clinically referred to as dental caries, is primarily caused by the interplay between dietary sugars, oral bacteria, and the resultant acid production that demineralizes tooth enamel. The causes overview includes the presence of specific bacteria types, particularly Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus, which metabolize fermentable carbohydrates to produce acids. This acidic environment leads to the progressive breakdown of the tooth’s mineral structure. Streptococcus mutans initiates demineralization, while Lactobacillus species contribute to its progression. The dynamic process of demineralization and remineralization is disrupted when acid production surpasses the protective effects of saliva and fluoride. Other contributing factors in the causes overview include poor dietary choices, inadequate oral hygiene, and reduced salivary flow, collectively exacerbating the risk of tooth decay.
The Importance of Regular Brushing and Flossing
Effective oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing and flossing, are critical in the prevention of tooth decay. Research indicates that employing proper brushing techniques, which include using a fluoride toothpaste and brushing for a minimum of two minutes twice daily, markedly reduces plaque accumulation. Additionally, daily flossing is essential for removing interdental plaque and debris that a toothbrush cannot reach, thereby mitigating the risk of decay in these areas.
Technique for Effective Brushing
Mastering the technique of brushing is paramount in the prevention of tooth decay, serving as a frontline defense against plaque accumulation. The American Dental Association (ADA) recommends brushing with a toothbrush held at a 45-degree angle to the gums, allowing bristles to reach the gingival margin, where plaque accumulation is most prevalent. Effective brushing techniques involve short, controlled strokes, ensuring coverage of all tooth surfaces, including occlusal, lingual, and buccal areas. Emphasizing gentle, circular movements can enhance plaque removal while minimizing enamel abrasion. Additionally, the ADA suggests a duration of at least two minutes per session, twice daily, to maintain ideal oral hygiene. Consistent implementation of these techniques can greatly reduce the incidence of dental caries and periodontal disease.
Benefits of Daily Flossing
While often overlooked in daily oral hygiene routines, flossing plays a critical role in preventing tooth decay and gum disease. Research indicates that integrating effective flossing techniques into one’s daily routine can remove plaque and food particles from interdental spaces that brushing alone cannot reach. The mechanical action of flossing disrupts dental plaque biofilms, reducing the risk of caries and periodontal disease. Evidence suggests that flossing daily is associated with improved oral health outcomes, as it helps maintain gum health and prevents the progression of gingivitis. The American Dental Association recommends the use of a gentle sawing motion to effectively clean between teeth without causing trauma to gingival tissues. Consequently, adopting proper flossing techniques is imperative for extensive oral hygiene.
Choosing the Right Toothpaste and Mouthwash
Selecting appropriate toothpaste and mouthwash is critical to preventing tooth decay, as these products play a significant role in oral hygiene by providing essential fluoride and antibacterial agents. Toothpaste ingredients such as calcium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, and triclosan work synergistically to remove plaque, neutralize acids, and inhibit bacterial growth. Additionally, the inclusion of xylitol promotes salivary flow and reduces cariogenic bacteria. Mouthwash types vary in their antimicrobial efficacy, with alcohol-based formulations offering enhanced bacterial reduction, while alcohol-free options cater to individuals with sensitivities. Chlorhexidine gluconate and essential oils in mouthwashes provide extensive bactericidal action, further preventing plaque accumulation. Evidence supports the regular use of these oral care products to maintain peak oral health and impede the progression of tooth decay.
The Role of Fluoride in Preventing Decay
Fluoride plays an instrumental role in the prevention of tooth decay, working in tandem with other oral care products to enhance dental health. Recognized for its ability to remineralize enamel, fluoride benefits are well-documented in dental literature. It facilitates the repair of microscopic lesions in tooth enamel, thereby impeding the demineralization process and reducing decay risk. Fluoride sources vary, encompassing public water supplies, dental products like toothpaste and mouth rinses, and professional treatments from dental practitioners. The incorporation of fluoride into daily oral hygiene routines has been shown to considerably decrease the incidence of cavities. Furthermore, fluoride’s antimicrobial properties help inhibit the proliferation of cariogenic bacteria, thereby contributing to an overall reduction in oral disease burden.
How Your Diet Affects Dental Health
A balanced diet is integral to maintaining ideal dental health, as it influences both the development and prevention of tooth decay. Nutritional choices impact oral microbial activity, which plays a vital role in caries formation. Diets high in fermentable carbohydrates increase the risk of demineralization due to acid production by oral bacteria. Conversely, incorporating healthy snacks, such as fiber-rich fruits and vegetables, can enhance salivary flow and mechanically cleanse teeth. Additionally, sugar alternatives, like xylitol, are beneficial as they do not contribute to acidogenic bacterial metabolism and may even inhibit cariogenic bacteria. Clinical studies underscore that a well-regulated diet, emphasizing nutrient-dense foods and minimal refined sugars, supports oral health and reduces the risk of dental caries.
Recognizing Early Signs of Tooth Decay
The intricate relationship between diet and dental health sets the stage for understanding the early indicators of tooth decay. Initial manifestations of tooth decay are subtle yet clinically significant. Early symptoms include localized tooth sensitivity, particularly in response to thermal stimuli or sweet food consumption. Visual indicators often present as white spot lesions on the enamel, signaling subsurface demineralization. Such lesions are typically opaque, contrasting with the surrounding healthy enamel, and may progress to cavitation if not addressed. Radiographic examination may reveal interproximal decay not visible to the naked eye, emphasizing the importance of regular dental assessments. Recognizing these early warning signs is essential for implementing timely interventions, thereby preventing the advancement of decay into more extensive dental pathology.

The Benefits of Dental Sealants
Dental sealants provide a protective barrier application that considerably reduces the risk of tooth decay by obstructing food particles and bacteria from settling in the grooves of the teeth. Studies have demonstrated the cavity prevention effectiveness of sealants, showing a reduction in decay incidence by up to 80% in molars. As a long-lasting dental solution, sealants can remain effective for several years, making them an essential component of preventative oral health care.
Protective Barrier Application
Applying a protective barrier in the form of dental sealants greatly reduces the risk of tooth decay, especially on the occlusal surfaces of molars and premolars where cavities commonly form. Dental sealants act as protective coatings that block food particles and bacteria from penetrating the tooth enamel. These barrier methods are particularly effective in young children and adolescents, whose newly erupted permanent teeth are more susceptible to decay. The sealants are composed of a resin material that adheres to the tooth surface, creating a physical shield against cariogenic activity. Clinical studies have demonstrated that the application of sealants can reduce caries incidence by up to 50%, underscoring their efficacy. By preventing demineralization, sealants serve as a preventive measure in maintaining oral health.
Cavity Prevention Effectiveness
Evidence underscores the importance of dental sealants in preventing cavities, highlighting their role as an effective measure against tooth decay. Dental sealants act as a physical barrier, reducing cavity risk by protecting occlusal surfaces from cariogenic bacteria and food particles. Studies indicate that sealants can lower the incidence of cavities by up to 80% in the first two years after application, thereby proving their efficacy as a prevention strategy. Sealant application is particularly beneficial for children and adolescents, whose molars and premolars are susceptible to carious lesions. The non-invasive nature of sealant placement further reinforces its value in thorough oral health care plans. These attributes establish dental sealants as a critical component in reducing cavity prevalence and enhancing preventive dental care.
Long-lasting Dental Solution
A pivotal advancement in preventive dentistry, dental sealants offer a durable solution for maintaining oral health by effectively safeguarding teeth from decay over an extended period. These thin, plastic coatings are professionally applied to the occlusal surfaces of molars and premolars, providing a physical barrier against cariogenic bacteria and acids. Research indicates that sealants reduce the risk of decay by nearly 80% in molars, substantiating their efficacy as a preventive measure. While natural remedies and holistic approaches to oral health emphasize balance and preventive care, dental sealants complement these by offering a scientifically validated method to protect vulnerable tooth surfaces. Their non-invasive application aligns with holistic principles by preserving natural tooth structure, enhancing dental health without altering the body’s innate processes.
When to Schedule a Dental Check-Up
Scheduling regular dental check-ups is a critical component in the prevention and management of tooth decay. Evidence suggests that an ideal check-up frequency is biannual for most individuals, although high-risk patients may require more frequent visits. Regular appointments facilitate early detection of dental caries and other oral pathologies, thereby enabling timely intervention. Dentists provide tailored recommendations based on individual risk assessments, which consider factors such as oral hygiene practices, dietary habits, and medical history. Appointment reminders, whether through digital alerts or traditional methods, serve as an effective strategy to enhance adherence to scheduled visits. By maintaining consistent dental evaluations, patients can greatly mitigate the progression of tooth decay and preserve overall oral health. The strategic timing of check-ups is paramount in sustaining ideal dental wellness.
Exploring Advanced Treatments for Tooth Decay
As dental technology continues to evolve, advanced treatments for tooth decay are becoming increasingly available, offering promising alternatives to traditional methods. Among these innovations, laser treatments have gained attention for their precision in targeting decayed tissue while preserving healthy tooth structure. Clinical studies have shown that laser treatments can reduce bacterial load and debride carious lesions effectively, thereby minimizing discomfort and recovery time for patients. Additionally, remineralization techniques are being explored as a preventive strategy, aiming to restore mineral content in early carious lesions. This approach utilizes bioactive materials, such as calcium phosphates and fluoride, to enhance enamel repair and halt the progression of decay. These advancements underscore a shift towards minimally invasive dentistry, prioritizing tooth conservation and patient comfort.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Stress Contribute to Tooth Decay?
Research indicates that stress can indirectly contribute to tooth decay by impairing immune function and promoting poor oral hygiene habits. Effective stress management strategies, combined with rigorous oral hygiene practices, are essential in mitigating the risk of dental caries.
Are There Any Natural Remedies to Stop Tooth Decay?
The inquiry concerns natural remedies for tooth decay prevention. Evidence suggests that oil pulling with coconut oil and using herbal toothpaste containing neem or clove can help inhibit bacterial growth, thereby potentially decelerating the progression of dental caries.
What Are the Genetic Factors Influencing Tooth Decay Risk?
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in tooth decay risk, with hereditary factors influencing enamel strength, salivary composition, and oral bacteria profile. Studies show variations in genes related to immune response and mineralization can affect susceptibility to decay.
How Does Smoking Impact Tooth Decay Progression?
Smoking effects include reduced saliva production and compromised immune response, accelerating tooth decay progression. Poor oral hygiene exacerbates these effects, leading to increased bacterial growth and enamel erosion, ultimately worsening dental health and increasing the risk of cavities.
Is Tooth Decay Linked to Other Health Conditions?
Tooth decay is linked to various health conditions. Oral bacteria associated with decay can contribute to systemic diseases such as cardiovascular issues and diabetes. Evidence suggests a bidirectional relationship between oral health and these systemic conditions.