Dental implants, a common solution for tooth loss, boast high biocompatibility and success rates due to materials like titanium and zirconia. These materials undergo rigorous testing to minimize adverse reactions. Advanced surgical techniques and imaging enhance precision, reducing complications. However, individual patient health factors, such as bone density, can impact outcomes. Thorough preoperative assessments and meticulous postoperative care are paramount to minimizing risks like infection or implant failure. Explore how these elements contribute to the safety of dental implants.
Understanding Dental Implants: What Are They?
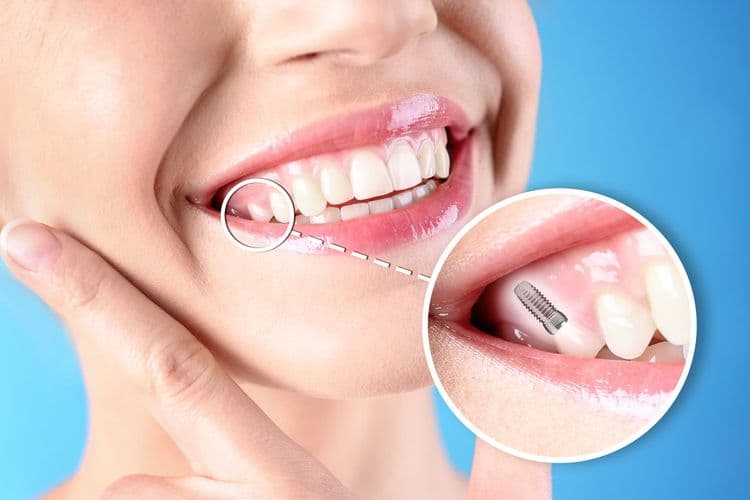
Dental implants, a sophisticated prosthetic solution for tooth replacement, consist of artificial tooth roots made from biocompatible materials such as titanium. These implants serve as a foundation for fixed or removable replacement teeth. There are various dental implant types, including endosteal and subperiosteal implants, each suited for different anatomical and clinical scenarios. The endosteal implant, the most prevalent type, is surgically placed into the jawbone, while subperiosteal implants rest on the bone under the gum tissue. Clinical studies consistently report high implant success rates, with endosteal implants demonstrating a success rate exceeding 95% over a five-year period. Such success is attributed to osseointegration, where the implant fuses with the bone, providing stability and functionality comparable to natural teeth.
The Procedure: How Dental Implants Are Placed
The placement of dental implants involves a meticulously planned surgical procedure where the implant is inserted into the jawbone. Initial evaluation includes radiographic imaging to assess bone density and structure, ensuring ideal conditions for implant placement. The surgical techniques employed vary, but commonly, a pilot hole is first drilled at the edentulous site to guide the implant. Precision instruments are utilized to expand this hole, accommodating the implant’s dimensions. Osseointegration, a critical phase, occurs as the titanium implant integrates with the surrounding bone tissue. During this period, temporary prosthetics may be used. The final stage involves attaching an abutment and securing the prosthetic crown. This evidence-based approach underscores the importance of sterile techniques and precision in achieving successful outcomes.
Assessing the Benefits of Dental Implants
Dental implants provide significant advantages regarding long-term oral health by maintaining alveolar bone integrity and preventing adjacent teeth from shifting. Additionally, they markedly enhance chewing efficiency, which is vital for ideal nutrient absorption and overall digestive health. Evidence-based studies consistently demonstrate the superior functional and physiologic outcomes of dental implants compared to traditional dentures or bridges.
Long-Term Oral Health
When considering the long-term impact of dental implants on oral health, it is essential to evaluate their benefits through rigorous clinical evidence. Dental implants have been shown to positively influence gum health by minimizing the risk of periodontal disease. The integration of implants with the jawbone promotes stability, thereby reducing bone resorption and preserving bone density. Studies indicate that implants can maintain alveolar bone levels, preventing the deterioration commonly associated with tooth loss. In addition, implants provide a stable foundation for prosthetic teeth, which supports the surrounding structures and protects against further oral complications. Clinical trials consistently demonstrate that, when properly maintained, dental implants offer a reliable solution for restoring function and aesthetics, consequently contributing considerably to long-term oral health stability.
Enhanced Chewing Efficiency
Beyond their role in maintaining long-term oral health, dental implants greatly enhance chewing efficiency, a critical aspect of oral functionality. This improvement is largely attributed to the restoration of ideal chewing dynamics and increased bite force. Dental implants are anchored securely into the jawbone, mimicking the natural tooth root structure. This secure integration allows for a more effective transfer of bite force, enabling individuals to process a wider variety of foods with greater ease. Clinical studies have demonstrated that individuals with dental implants exhibit considerably improved masticatory performance compared to those with traditional dentures. The enhanced chewing dynamics afforded by implants not only promote better digestion but also contribute to overall nutritional intake, underscoring their role in thorough oral rehabilitation.
Potential Risks and Complications
Numerous potential risks and complications are associated with dental implant procedures, warranting careful consideration by both clinicians and patients. Infection risks are paramount, as microbial colonization at the surgical site can lead to peri-implantitis, potentially compromising osseointegration. The prevalence of postoperative infections necessitates stringent aseptic protocols and vigilant monitoring. Recovery complications, such as delayed healing and implant failure, may arise from factors like inadequate bone density or improper surgical technique. These complications can considerably impact the long-term success of the implant, requiring interventions such as bone grafting or implant revision. Additionally, patients may experience nerve damage, sinus complications, or mechanical failures, underscoring the importance of thorough preoperative assessment and tailored treatment planning to mitigate potential adverse outcomes.
Factors Affecting the Safety of Dental Implants
The safety of dental implants is greatly influenced by implant material compatibility and the precision of the surgical procedure. Biocompatibility of implant materials is vital to minimizing adverse tissue reactions and ensuring osseointegration. In addition, meticulous surgical technique, guided by advanced imaging technologies, is essential to prevent complications such as nerve damage and implant failure.
Implant Material Compatibility
While the success of dental implants often hinges on various factors, the compatibility of implant materials with biological tissues is paramount to ensuring safety and efficacy. Implant material types, typically titanium and zirconia, are selected based on their proven biocompatibility and mechanical stability. Biocompatibility testing is a critical procedure that evaluates potential adverse reactions between implant materials and human tissues. This testing aims to identify any cytotoxic, immunogenic, or inflammatory responses that could compromise implant integration. Titanium, due to its favorable osseointegration properties and minimal reactivity, remains the gold standard. Zirconia, known for its aesthetic appeal and hypoallergenic nature, is gaining traction as an alternative. Ensuring material compatibility through rigorous testing helps mitigate risks of implant failure and enhances long-term success rates.
Surgical Procedure Precision
Establishing material compatibility is only one facet of guaranteeing dental implant safety; surgical procedure precision plays a pivotal role in successful outcomes. The meticulous execution of surgical techniques is vital for minimizing complications and optimizing implant longevity. Precision tools, such as computer-guided surgical systems, enhance accuracy in implant placement, reducing risks of nerve damage and improper angulation. Evidence-based practices emphasize the importance of using advanced imaging modalities, like cone beam computed tomography (CBCT), to obtain detailed anatomical insights. These techniques enable clinicians to plan and execute procedures with heightened precision. In addition, the integration of stereolithographic guides has demonstrated improved accuracy in implant positioning. Mastery of these precision tools and techniques is essential for dental professionals to guarantee the safety and efficacy of implant procedures.
Innovations in Dental Implant Technology
Advancements in dental implant technology are revolutionizing the field by enhancing both patient outcomes and procedural efficiency. Digital advancements, such as computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) systems, facilitate precise implant planning and placement, reducing surgical time and improving osseointegration success rates. Moreover, innovations in biomechanical engineering are optimizing implant materials and designs. For instance, surface modifications with enhanced roughness and bioactive coatings promote superior bone-implant integration. Additionally, the development of zirconia implants offers biocompatibility and aesthetic advantages over traditional titanium implants. Evidence from clinical trials indicates improved long-term stability and reduced peri-implantitis risk with these innovations. Collectively, these technological strides underscore a paradigm shift in implantology, contributing to safer, more effective solutions for dental rehabilitation.
Comparing Dental Implants to Other Tooth Replacement Options
When evaluating tooth replacement options, dental implants stand out due to their structural and functional advantages over traditional methods such as dental bridges and dentures. Implants offer osseointegration, providing a stable and durable foundation by fusing with the jawbone, unlike dental bridges which rely on adjacent teeth for support, potentially compromising their integrity. In a dental bridges comparison, implants minimize bone resorption, preserving jawbone health. Dentures alternatives, such as implants, eliminate issues of slippage and discomfort associated with removable prosthetics, enhancing masticatory efficiency and speech. Clinical studies demonstrate that dental implants exhibit superior longevity and patient satisfaction rates. Though initial costs are higher, implants present a cost-effective solution over time by reducing the need for replacements and adjustments.
Insights From Dental Professionals on Implant Safety
Dental implants not only provide structural advantages over traditional tooth replacement options but also raise important considerations regarding safety, as highlighted by dental professionals. Critical to implant safety is the emphasis on implant maintenance, which involves routine professional evaluations, radiographic assessments, and meticulous oral hygiene practices. Dental professionals underscore that patient education is paramount in fostering an understanding of potential complications, such as peri-implantitis, and the importance of regular follow-ups. Evidence suggests that patients who are well-informed about their implant maintenance regimens exhibit higher success rates and longevity of the implants. Clinicians advocate for ongoing education sessions to reinforce the significance of compliance in maintaining oral health, thereby minimizing risks and ensuring ideal outcomes in implant therapy.
Real Patient Stories: Experiences With Dental Implants
Many patients have shared their diverse experiences with dental implants, shedding light on both the complexities and successes associated with this procedure. Patient testimonials reveal a spectrum of outcomes, reflecting individual anatomical and physiological variations. Personal journeys often highlight initial challenges, such as osseointegration issues or peri-implantitis, yet also describe long-term satisfaction with improved masticatory function and aesthetics.
These narratives underscore the importance of personalized treatment plans, emphasizing the role of thorough preoperative assessments and postoperative care in mitigating complications. Evidence-based reviews consistently show high success rates, yet patient experiences indicate that adherence to clinical guidelines and patient-specific factors are pivotal. Such stories contribute valuable insights into the multifaceted nature of dental implants, guiding clinicians in optimizing patient outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Do Dental Implants Typically Last?
Dental implants typically exhibit a longevity of 10-15 years, contingent on factors such as oral hygiene, regular dental check-ups, and lifestyle habits. Maintenance tips include daily flossing, thorough brushing, and avoiding excessive forces or smoking.
Can Dental Implants Cause Metal Allergies?
Dental implants can potentially cause metal sensitivity due to their implant materials, typically containing titanium alloys. Although rare, hypersensitivity reactions may occur, necessitating thorough preoperative assessments and consideration of alternative materials for susceptible individuals.
Is the Implant Procedure Painful?
The implant procedure’s discomfort is typically minimized through effective pain management strategies, including anesthesia. Post-operative pain varies, but is generally manageable and temporary, with the recovery process involving gradual reduction in discomfort as healing progresses.
Are There Dietary Restrictions After Getting Implants?
Post-implantation, patients should adhere to a soft foods regimen to prevent complications. Emphasis on hydration is essential for ideal healing. Clinical guidelines suggest avoiding hard or sticky foods to guarantee implant stability and promote recovery.
Can Smokers Get Dental Implants?
Smokers considering dental implants should be aware that smoking effects may impair the healing process. Clinical studies indicate that tobacco use can lead to complications, reduced osseointegration, and increased risk of implant failure, necessitating thorough preoperative evaluation.